As is well known, coatings generally consist of four basic components: film-forming substances, pigments, solvents, and additives. Pigments primarily provide color and coverage in coatings. Pigments can be divided into coloring pigments and functional pigments (also known as fillers). Coloring pigments provide color, while functional pigments, like Calcium Carbonate in Pigments, enhance thickness and functionality. Non-metallic mineral powders, like Calcium Carbonate in Pigments, are mainly used as fillers in coatings.
Calcium Carbonate in Pigments is the most commonly used non-metallic mineral filler due to its high cost-performance ratio, which is fine, uniform, with high whiteness and excellent optical properties. When added to water-based coatings, Calcium Carbonate in Pigments improves reinforcement, transparency, thixotropy, and leveling. It significantly enhances stain resistance, scrubbability, adhesion, and prevents settling in the coating.
Based on production process and performance, Calcium Carbonate in Pigments can be categorized into heavy calcium carbonate, light calcium carbonate, and nano-calcium carbonate.

Heavy Calcium Carbonate
Heavy calcium carbonate is the most important filler in the coating industry. It is cheap, easily available, and has good whiteness, low oil absorption, moderate specific gravity, and good dispersibility. It helps reduce costs significantly and is widely used in latex paint, waterproof paint, light anti-corrosion industrial paint, floor paint, wood paint, and powder coatings. However, heavy calcium carbonate varies due to differences in raw ores, purity, particle density, bulk density, and more. This affects its hiding power, washability, glossiness, processing fluidity, and stability in coatings.
By comparing the application of different heavy calcium carbonates, several results were observed. In interior wall latex paint, heavy calcium carbonate from large calcite has better contrast ratio and wash resistance than small calcite and dolomite. Heavy calcium carbonate from dolomite in inorganic interior wall coatings has poor stability and is unsuitable for use. On the other hand, heavy calcium carbonate from calcite shows better stability in inorganic interior wall coatings. In polyester powder coatings, heavy calcium carbonate from dolomite has significantly better processability, paint film gloss, whiteness, and contrast ratio. This is compared to small calcite and large calcite products of the same specifications.

Light Calcium Carbonate
Light calcium carbonate is characterized by low density and fine particles but has poorer stability. Due to its excellent suspension and dry film opacity, it was widely used in latex paints in the past. It effectively improves the storage suspension and dry coverage of coatings. However, if the production process of light calcium carbonate is not well controlled, excessive free calcium ions can often lead to emulsification breakdown, affecting the stability of the paint. As a result, its use in architectural coatings has decreased since the introduction of calcined kaolin. Additionally, due to its higher oil absorption and poor flowability, light calcium carbonate is also used in textured powder coatings.
Light calcium carbonate production process:
Limestone → Calcination → Digestion → Refining → Concentration and Temperature Adjustment → Carbonation → Filtration → Drying → Grinding and Classification → Packaging
Nano Calcium Carbonate
Compared to heavy calcium or ordinary light calcium, nano calcium carbonate not only provides better reinforcement in coatings but also offers significant advantages in improving gloss, transparency, quick drying, and stability. It can also help suspend heavier components like titanium dioxide, preventing settling.
Nano calcium carbonate has high filling performance. It has an excellent whitening effect. It enhances coating durability. As a result, it is widely used in interior and exterior wall paints. It is also used in wood coatings and other applications. It can improve stain resistance and crack strength of coatings.
Furthermore, nano calcium carbonate can enhance the washability and stability of coatings through steric hindrance effects. In high-end automotive underbody PVC paints, it alters the thixotropy of PVC paints, improving impact strength and spray curing speed.
More importantly, nano calcium carbonate can significantly replace expensive titanium dioxide and high-cost colloidal calcium, reducing the need for base adhesives and other additives, thereby lowering production costs.
In addition, nano calcium carbonate holds promising applications in specialized fields such as anti-corrosion coatings, protective coatings, and specialty industrial coatings. However, nano calcium carbonate faces challenges like agglomeration and difficulty in controlling crystal form, which can affect product stability. These issues can be addressed through powder modification techniques.
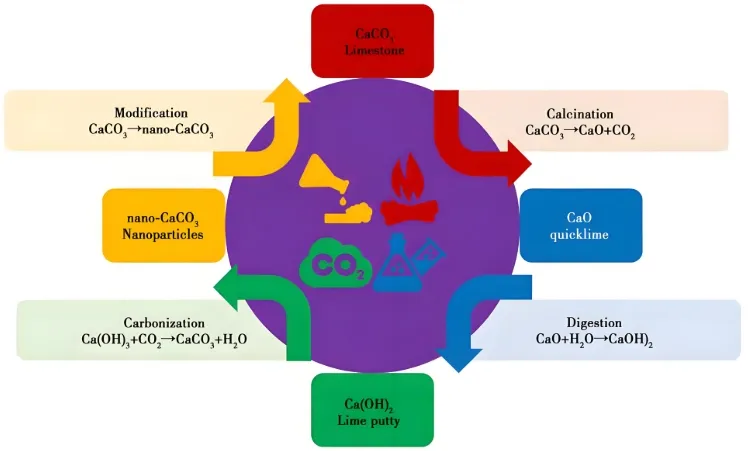
Surface Modification
With the continuous development of modifier types and modification equipment, more and more modified calcium carbonate products are being applied in the coating industry to enhance product functionality.
- Inorganic materials, like sodium hexametaphosphate, are used as modifiers. Mechanical chemical forces combine with hydrothermal methods. This modifies ultrafine calcium carbonate. Significant improvements in dispersion, hardness, and mechanical properties are achieved. These enhancements benefit water-based plastic coatings.
- Surface modification of calcium carbonate with KH-560 enhances the hardness, adhesion, and impact resistance of wood coatings. It improves the compatibility, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability of epoxy coatings.
- Modified heavy calcium carbonate with stearic acid and coupling agents improves processability and gloss. It outperforms ordinary calcium carbonate in epoxy polyester powder coatings. Calcium carbonate modified with coupling agents also enhances the impact strength and adhesion of the coating film.

Conclusion
Calcium carbonate plays a pivotal role in the pigment industry, offering significant benefits as a functional filler. Its versatility enhances opacity, improves dispersibility, and lowers production costs. Calcium carbonate is an invaluable component in coatings and paints. Whether in heavy, light, or nano form, it drives innovation in pigments. It offers both performance and economic advantages for manufacturers. As the demand for higher-quality, cost-effective solutions increases, the role of calcium carbonate in pigments will only grow more essential.
Epic Powder
Epic Powder, 20+ years of work experience in the ultrafine powder industry. Actively promote the future development of ultra-fine powder, focusing on crushing,grinding,classifying and modification process of ultra-fine powder. Contact us for a free consultation and customized solutions! Our expert team is dedicated to providing high-quality products and services to maximize the value of your powder processing. Epic Powder—Your Trusted Powder Processing Expert !
