Nano calcium carbonate refers to calcium carbonate microparticle aggregates with a particle size between 1-100 nm. Particle size reduction alters the crystal structure and surface electronic structure. This creates surface effects, size effects, and macroscopic quantum tunneling effects not present in larger particles.
Production
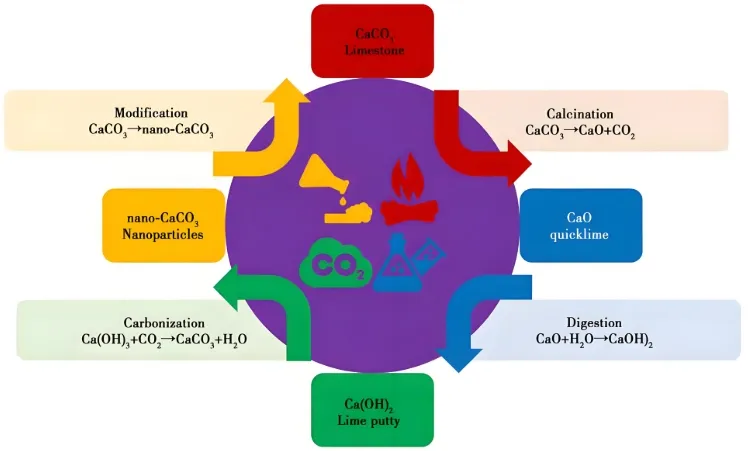
Currently, carbonation is the main method for industrial production of nano-calcium carbonate. Its raw material is mainly limestone with a high calcium carbonate content. The raw material undergoes calcination, digestion, carbonation, modification, dispersion, drying, and packaging to obtain the final product. The carbonation process involves four main chemical reactions: calcination, digestion, carbonation, and modification. The key step in producing nano-calcium carbonate via carbonation is the carbonation reaction. According to the interaction between Ca(OH)2 slurry and CO2, the methods include batch carbonation, multi-stage spray carbonation, and supergravity carbonation.
Batch Carbonization
Improved based on the production of light calcium carbonate, CO2 is introduced from the bottom of the tower. During carbonation, crystal control agents are added to control crystal form and particle size. Precipitating agents are added to generate precipitation and separation, resulting in nano-calcium carbonate with different crystal sizes.
Multi-stage Spray Carbonization Method

Multiple carbonation towers are typically used to obtain nano-calcium carbonate through a gas-liquid reaction. First, a slurry of Ca(OH)2 and Al2(SO4)3 or ZnSO4 is sprayed in droplet form from the top of the first carbonation tower. CO2 is introduced from the bottom of the tower, initiating the carbonation reaction to produce carbonation liquid. Next, the carbonation liquid is sprayed in droplet form from the top of the second carbonation tower. CO2 is introduced from the bottom of the tower, triggering a secondary carbonation reaction to produce nano-calcium carbonate.
High Gravity Carbonization
A powerful centrifugal force field is generated by the high-speed rotation of the packing bed, creating a supergravity environment. This causes the emulsion to break into very small droplets, greatly increasing the gas-liquid contact area and enhancing carbonation speed. Additionally, the emulsion is highly dispersed in the high-speed rotating packing bed, limiting crystal growth. Even without adding crystal control agents, the particle size of the nano-calcium carbonate produced can reach 15-30 nm.
Application
Plastics and Rubber Fields (structural reinforcement)
The addition of nano-calcium carbonate in composite materials is typically only 3%-5%, but its reinforcing effect is equivalent to about 30% glass fiber or mineral reinforcement. The nanocomposite of nano-calcium carbonate and organic polymers combines the dimensional stability and thermal stability of inorganic materials with the dielectric properties of organic polymers. Additionally, the composite material has high melt strength, low viscosity, and fast crystallization speed, which is beneficial for processes like injection molding, extrusion, and blow molding of organic polymers.
Coating, Papermaking, Lubricating Oil
- When added to organic or water-based coatings, the resulting coating has smooth, uniform, fast-drying, and high whiteness characteristics. It can replace expensive titanium dioxide and high-cost colloidal calcium, reducing the binder usage in the base material. This helps suspend heavier rutile powder and prevents sedimentation, improving brushability and stability through steric hindrance effects. It is suitable for high-end automotive topcoats and chassis coatings.
- Modified nano-calcium carbonate has good dispersibility and, when used in papermaking, increases brightness and opacity. It improves paper smoothness and flexibility, enhancing ink absorption and retention, making it suitable for high-quality coated paper.
- When added to lubricating oil, nano-calcium carbonate forms a monomolecular protective film on the metal surface via electrostatic adsorption. This improves the anti-wear and friction-reducing properties of the lubricating oil.
Biopharmaceuticals
Nano-calcium carbonate also has good biocompatibility and biodegradability, giving it huge potential in pharmaceuticals delivery, tissue repair, and biosensing applications. Especially in the development of anticancer targeted pharmaceuticals, nano-calcium carbonates can serve as a carrier for both hydrophobic and hydrophilic pharmaceuticals. Its slow biodegradation allows the pharmaceuticals to stay in the lesion area longer, ensuring sustained pharmaceuticals release.
Conclusion
Nano-calcium carbonate, with its unique physicochemical properties, continues to innovate and optimize production processes. It demonstrates outstanding application value across various fields. With ongoing technological advancements and deeper research, nano-calcium carbonate is expected to expand into more emerging areas. It will bring breakthroughs and surprises to material science, biomedicine, and other industries. This will continue to drive high-quality development in related industries.
Epic Powder

Epic Powder, 20+ years of work experience in the ultrafine powder industry. Actively promote the future development of ultra-fine powder, focusing on crushing,grinding,classifying and modification process of ultra-fine powder. Contact us for a free consultation and customized solutions! Our expert team is dedicated to providing high-quality products and services to maximize the value of your powder processing. Epic Powder—Your Trusted Powder Processing Expert !
